IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) is a critical process for managing the lifecycle of technology products in a way that maximizes value recovery while minimizing environmental impact and ensuring data security. In this blog post, we will define ITAD, discuss its importance, and highlight its benefits. Additionally, we will delve into the various types of IT assets involved and the lifecycle stages from procurement to disposal.
What is IT Asset Disposition?

IT Asset Disposition, commonly abbreviated as ITAD, refers to the comprehensive management strategy used to handle the disposal of obsolete or unwanted equipment in a safe and ecologically-responsible manner. ITAD encompasses a range of services that help organizations dispose of IT equipment without compromising data security and in compliance with environmental regulations.
The scope of ITAD extends beyond mere disposal; it involves the systematic process of recovering residual value from outdated hardware, ensuring data privacy through destruction or wiping, and ethically recycling materials to prevent environmental damage. Proper ITAD practices enable companies to mitigate risks associated with data breaches, legal penalties, and environmental harm.
Importance of ITAD in Managing the Lifecycle of Technology Products
The importance of IT Asset Disposition can hardly be overstated, especially in an era where technology evolves at an unprecedented pace. ITAD provides a structured approach to manage the end-of-life phase of IT assets, ensuring that they are handled responsibly. This process is crucial for:
- Data Security: Securely erasing sensitive information to protect against data breaches.
- Compliance: Adhering to legal standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and various environmental regulations.
- Value Recovery: Extracting maximum residual value from retired IT assets through resale or recycling.
- Sustainability: Promoting environmental sustainability by reducing e-waste and encouraging the recycling of electronic components.
Key Benefits of Effective ITAD Management
Effective ITAD management offers several tangible benefits that help organizations not only comply with legal requirements but also enhance their corporate reputation and operational efficiency:
- Risk Mitigation: Reduces the risk of data theft and ensures compliance with data protection laws, thereby safeguarding organizational reputation.
- Cost Savings: Minimizes costs associated with data breaches and legal penalties, while also optimizing the return on investment from outdated technology.
- Environmental Responsibility: Supports eco-friendly practices by ensuring proper recycling and disposal, thereby reinforcing the organization’s commitment to sustainability.
- Resource Efficiency: Helps in reallocating resources more efficiently by clearing out obsolete equipment and freeing up space and capital for newer technologies.
Why Understanding What is IT Asset Disposition Matters
Definition and Scope of ITAD
ITAD is not just about disposing of old equipment; it’s a strategic approach that encompasses several processes designed to handle IT assets securely and sustainably from the moment they are no longer needed. It involves detailed asset tracking, handling, and disposing of IT assets to ensure that all aspects of data security, environmental policy, and value recovery are addressed.
Types of Assets Included in ITAD
ITAD programs typically cover a wide range of IT equipment, including:
- Computers: Desktops and laptops that may contain sensitive data or proprietary software.
- Servers: Robust machines that often hold large volumes of critical business data and require careful decommissioning.
- Mobile Devices: Smartphones and tablets that are frequently upgraded and need secure data wiping before disposal.
- Peripheral Equipment: Printers, scanners, and other devices that are part of the IT infrastructure.
The Lifecycle of IT Assets from Procurement to Disposal
The lifecycle of IT assets includes several key phases:
- Procurement: Acquiring the IT hardware necessary for business operations.
- Deployment: Installing and configuring IT equipment for use.
- Maintenance: Ensuring IT assets are operational and resolving any issues.
- Decommissioning: Removing IT assets from active service when they are outdated or no longer needed.
- Disposition: The final phase, where ITAD practices are implemented to dispose of the equipment securely and responsibly.
Understanding these stages helps organizations plan their ITAD strategy effectively, ensuring that each phase is managed to optimize security, compliance, and value recovery.
In this part of our series, we explore the critical importance and processes of IT Asset Disposition (ITAD), a key business practice that supports legal compliance, data security, environmental sustainability, and financial efficacy. Further, we delve into the detailed steps of the ITAD process, ensuring organizations can implement these practices effectively.
Why ITAD Matters
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
ITAD is essential for compliance with a variety of legal and regulatory frameworks, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States. These regulations mandate strict standards for handling and disposing of data-bearing devices to protect personal and sensitive information.
GDPR Compliance
Under GDPR, organizations must ensure personal data is erased when it’s no longer necessary. ITAD plays a crucial role in data destruction, ensuring data on decommissioned IT assets is completely destroyed or irreversibly anonymized.
HIPAA Compliance
For healthcare organizations, HIPAA requires the protection of patient data, even during disposal. ITAD providers must therefore guarantee that all data is securely wiped from devices or physically destroyed in compliance with HIPAA’s disposal rules.
Data Security and Data Destruction Processes
Data security is a cornerstone of ITAD, as improper handling of data can lead to significant breaches and financial penalties. Effective ITAD programs include detailed processes for data destruction which may involve software wiping, degaussing (magnetic destruction), or physical destruction of hard drives and other storage media.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Practices
ITAD significantly contributes to environmental sustainability by promoting the responsible recycling and disposal of electronic waste, which contains potentially hazardous materials like lead and mercury. Practices such as refurbishing and recycling help reduce the environmental footprint and promote the reuse of valuable materials, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Cost Management and Recovery
Effective ITAD also offers financial benefits by allowing companies to recover value from outdated assets through resale or recycling. This cost recovery can offset the expense of new technology investments, making ITAD an economically wise strategy as well as an operational necessity.
The ITAD Process: What is IT Asset Disposition from Start to Finish
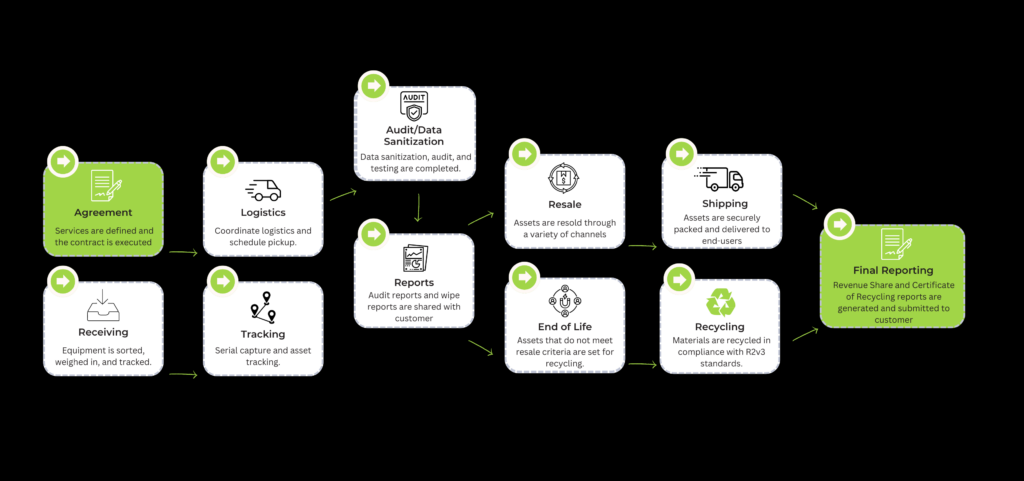
The ITAD process is a comprehensive approach to managing the end-of-life of IT assets, from collection to final disposition, ensuring data security, legal compliance, and minimal environmental impact.
What is IT Asset Disposition?
Overview of the Standard ITAD Process
The standard ITAD process involves several critical steps, each designed to handle different aspects of asset disposition:
- Collection and Logistics: Secure transportation of IT assets from the client’s site to the ITAD facility.
- Inventory and Auditing: Detailed documentation of all assets received to track each item throughout the disposition process.
- Data Destruction and Data Wiping: Implementation of data sanitization methods to securely erase or destroy data stored on devices.
- Refurbishing, Remarketing, and Recycling: Assessment and processing of IT assets for resale, donation, or recycling.
- Final Disposition: Ethical disposal of non-recoverable components in compliance with environmental regulations.
Detailed Description of Each Step
Collection and Logistics
Secure transport is essential to prevent theft or data leakage. ITAD providers typically use GPS-tracked and locked vehicles to transport assets directly from the business to the processing facility.
Inventory and Auditing
Upon arrival, each asset is logged and audited for specifications and condition. This step is crucial for tracking purposes and valuation for recovery.
Data Destruction and Data Wiping
Data on all devices is either completely destroyed using shredding methods or wiped using software techniques that meet international standards like NIST SP 800-88.
Refurbishing, Remarketing, and Recycling
Functional equipment is refurbished and sold in secondary markets, which helps in recovering value. Non-functional items are disassembled, and valuable materials are reclaimed for recycling.
Best Practices for Ensuring Security and Compliance Throughout the Process
To ensure that ITAD processes adhere to the highest standards of security and compliance, organizations should:
- Select Certified ITAD Providers: Only work with providers that have certifications such as R2, e-Stewards, or NAID.
- Audit ITAD Processes: Regularly review and audit the ITAD process to ensure compliance with internal policies and external regulations.
- Use Data Destruction Verification: Implement verification processes for data destruction, including certificates of destruction for auditable proof.
By understanding and implementing these steps and best practices, organizations can ensure that their ITAD process is secure, compliant, and effective.
In this continuation of our series, we explore the crucial aspects of selecting an ITAD provider and understanding the connection between ITAD practices and corporate social responsibility (CSR). We also look ahead to future trends in the ITAD industry.
Choosing an ITAD Provider
Choosing the right ITAD provider is a critical decision for organizations aiming to ensure compliance, data security, and environmental responsibility. This section outlines what to consider, the certifications to look for, and the questions to ask potential ITAD providers.
What is IT Asset Disposition? What to Look for in an ITAD Provider
When selecting an ITAD provider, key considerations include:
- Experience and Reputation: Look for providers with a solid track record and strong industry reputation.
- Security Measures: Ensure the provider uses robust security protocols throughout the ITAD process.
- Environmental Compliance: The provider should comply with local and international environmental regulations.
- Transparency and Reporting: Opt for providers who offer detailed reporting on every stage of the ITAD process for complete transparency.
- Value Recovery Options: Assess their ability to maximize financial return through refurbishing, resale, and recycling of assets.
Certifications and Standards

Certifications are indicators of an ITAD provider’s commitment to industry standards and best practices:
- R2 (Responsible Recycling): Focuses on safe and environmentally responsible recycling practices.
- e-Stewards: Enforces stringent environmental and data security standards in electronic waste management.
- NAID AAA Certification: Validates compliance with standards for data destruction processes.
Providers with these certifications are likely to adhere to higher standards of operation, ensuring secure and responsible ITAD practices.
Questions to Ask Potential ITAD Providers
When evaluating ITAD providers, consider asking the following questions:
- How do you ensure data security during the ITAD process?
- Can you provide details on your environmental compliance policies?
- What are your processes for asset tracking and reporting?
- How do you handle international shipments and global compliance?
- What are your certifications, and how often are they reviewed or renewed?
ITAD and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
ITAD plays a significant role in supporting CSR initiatives by promoting environmental sustainability and responsible data management.
How ITAD Supports CSR Initiatives
ITAD contributes to CSR in several ways:
- Environmental Stewardship: By properly recycling e-waste, ITAD helps companies minimize their environmental footprint.
- Data Protection: Ensuring secure data destruction protects customer information, supporting ethical business practices.
- Resource Recovery: Recycling parts of IT assets conserves resources and supports sustainability goals.
Future Trends in ITAD
Looking ahead, the ITAD sector is likely to evolve in several key areas:
- Increased Focus on Circular Economy: More companies will adopt circular economy principles, aiming to reuse and recycle IT assets as much as possible.
- Technology Integration: Advances in technology, such as AI and IoT, will enhance the efficiency and security of the ITAD process.
- Global Regulation Compliance: As data protection laws become more stringent worldwide, ITAD providers will need to ensure global compliance, particularly for multinational corporations.
By understanding these elements and future directions, organizations can better integrate ITAD into their overall business strategy, enhancing their CSR initiatives and ensuring compliance and sustainability in the digital age.
As we continue our comprehensive exploration of IT Asset Disposition, this installment will address the challenges faced by organizations in implementing effective ITAD strategies, discuss innovative solutions, and look into the future of ITAD.
Challenges and Solutions in ITAD
Common Challenges Organizations Face in ITAD
Organizations embarking on ITAD initiatives often encounter several significant challenges:
- Data Security Risks: Ensuring complete data destruction to prevent data breaches.
- Compliance with Diverse Regulations: Navigating the complex web of local, national, and international regulations.
- Logistical Complexity: Managing the logistics of collecting and processing IT assets from multiple locations.
- Cost Management: Balancing the costs associated with ITAD processes while maximizing the recovery value of assets.
Innovative Solutions and Emerging Technologies in ITAD
To address these challenges, the ITAD industry has turned to innovative solutions and technologies:
- Blockchain Technology: Enhances transparency and security in the ITAD process by providing a tamper-proof record of actions taken on each asset.
- Automation and Robotics: Streamlines processes such as data wiping and physical dismantling of devices, reducing human error and increasing efficiency.
- Advanced Data Wiping Software: Ensures data is irrecoverably destroyed, meeting stringent compliance requirements.
How to Overcome Obstacles in Implementing an Effective ITAD Strategy
Implementing an effective ITAD strategy involves several key practices:
- Partner with Certified ITAD Providers: Ensure that your ITAD provider holds relevant certifications and adheres to industry standards.
- Regular Training and Awareness: Keep your team informed about the latest ITAD practices and compliance requirements.
- Implement Rigorous Processes: Establish clear, standardized procedures for every phase of the ITAD process.
- Use Technology: Leverage technologies like cloud-based asset management systems to track IT assets throughout their lifecycle.
The Future of ITAD
Technological Advancements Influencing ITAD
The ITAD industry is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements:
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT technology helps track assets in real-time, making it easier to manage and dispose of IT assets securely.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI can predict the lifespan of assets and optimize the refurbishment and recycling process, enhancing the efficiency of ITAD programs.
The Evolving Regulatory Landscape
As data privacy and environmental issues gain prominence, regulatory frameworks are becoming stricter and more complex. Organizations must stay informed about these changes to ensure compliance in their ITAD practices.
Predictions for the ITAD Industry
- Growth in Demand: As more businesses recognize the importance of ITAD, demand for these services is expected to grow.
- Focus on Sustainability: There will be a greater emphasis on sustainable practices within ITAD, including increased reuse and recycling of IT assets.
- Integration with Global Business Strategies: ITAD will become an integral part of global business strategies, particularly in terms of risk management and CSR.
The global IT asset disposition (ITAD) market size and share is currently valued at USD 15,578.94 million in 2023. It is anticipated to generate an estimated revenue of USD 32,355.70 million by 2032, according to the latest study by Polaris Market Research. Besides, the report notes that the market exhibits a robust 8.5% Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) over the forecasted timeframe, 2024-2032.
IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) is crucial for enhancing data security, supporting environmental sustainability, and improving financial returns. As businesses continue to evolve in a digital-first world, adopting a strategic approach to ITAD is not just beneficial but necessary. To effectively manage the complexities of ITAD and ensure compliance with evolving regulations, we strongly recommend partnering with a professional ITAD service. For expert assistance and optimal ITAD solutions, contact Monmouth Wire Computer Recycling. This partnership will provide you with the expertise, technology, and processes needed to optimize your ITAD strategy and safeguard your business interests.

